What To Expect
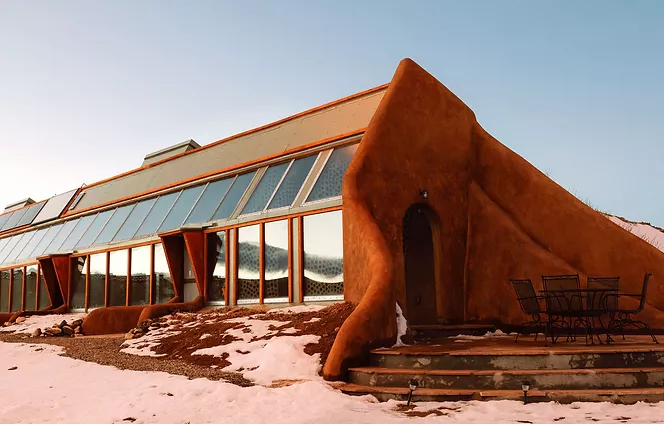

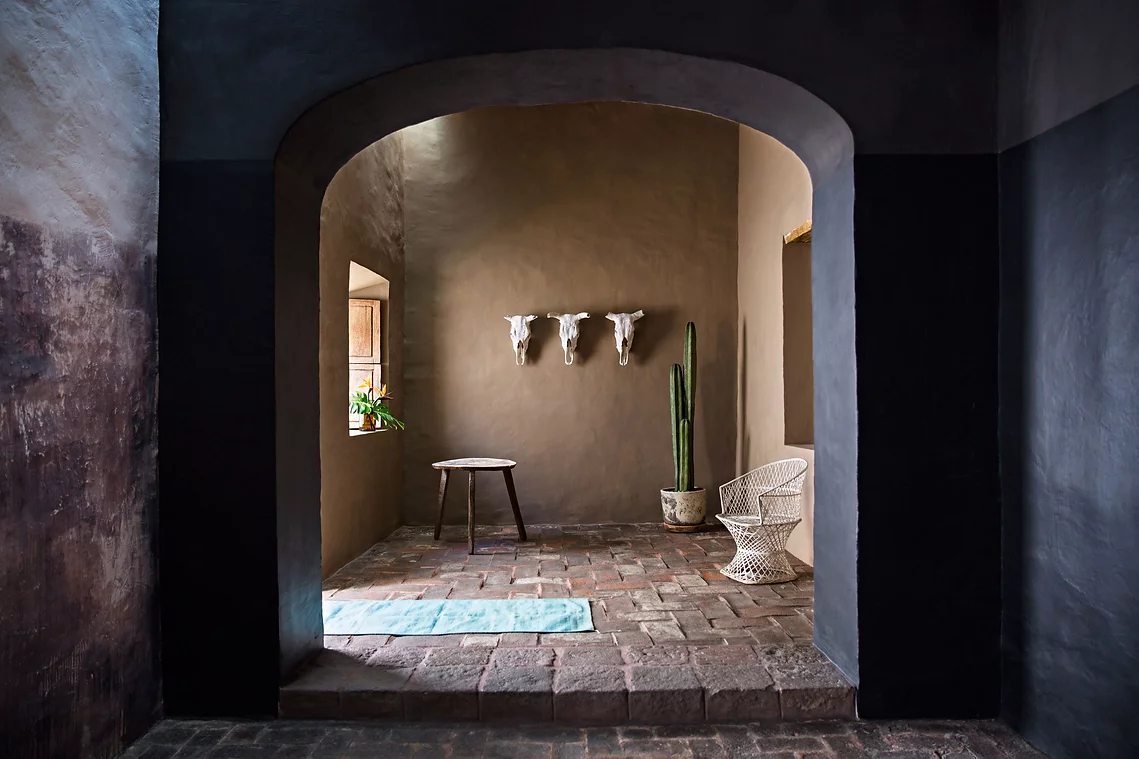
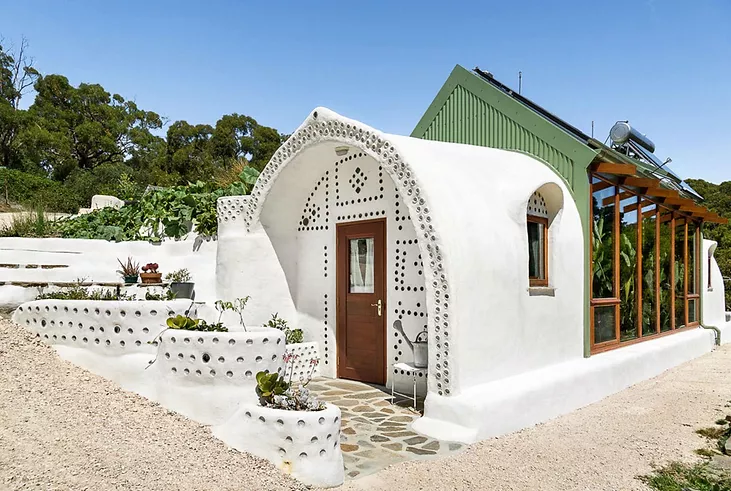
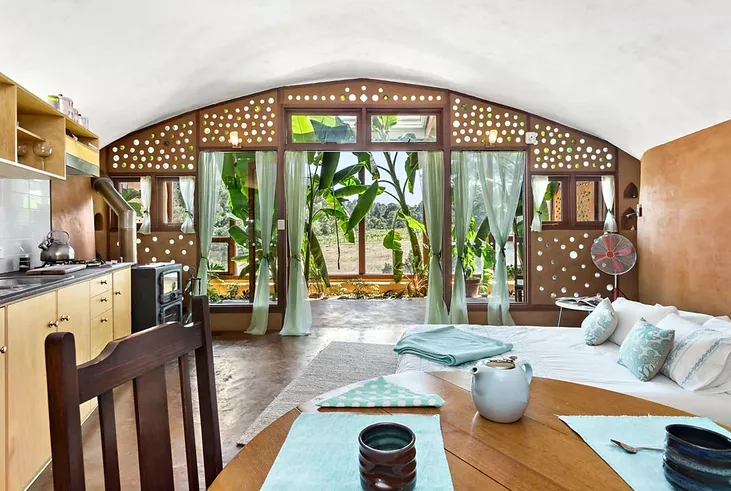
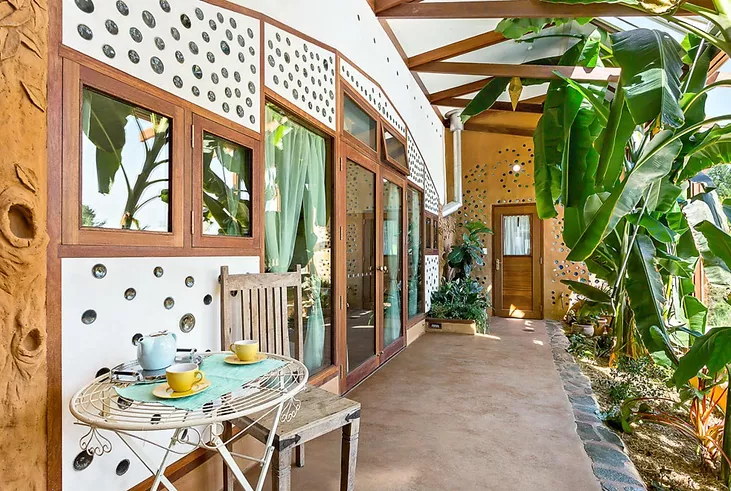
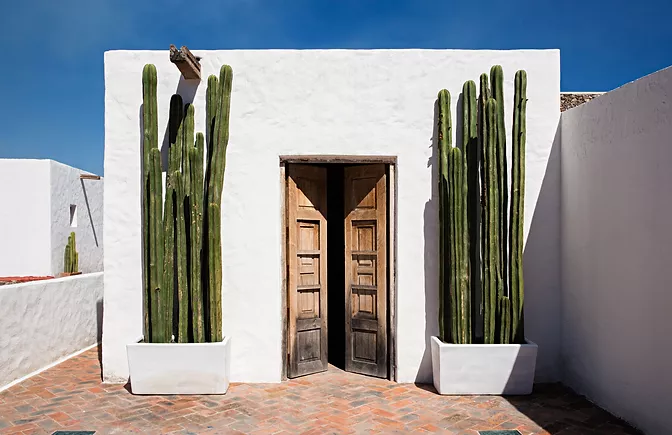
Earthship Homes
Earthship homes aim to meet basic human needs (shelter, heat, food, water, etc.) through self-sufficiency and sustainability.
Architect Michael Reynolds pioneered Earthship homes in the 1970s. His idea of Earthsip homes came from realizing the amount of rubbish piling up and the lack of affordable housing could be simultaenously addressed.
Principles of Earthship Homes






Image via The Boho Guide
Earthships have their name because they operate autonomously from outside sources, just as ships do when they are sailing the open seas. These 6 basic principles that guide Earthship homes design.
Click on each principle to read more about how these components of Earthship homes function and how to install them.
Costs and Other Considerations for Earthships
Generally, Earthships can cost between $20,000 to $500,000, depending on the size of your home, amount of labor you need and other necessary inclusions.
If you want to build one yourself, Earthship Biotecture offers a one-month training program for $2,500. Read more about costs here.
Click here to read some things to consider for an Earthship home as well as advatanges and disadvantages.
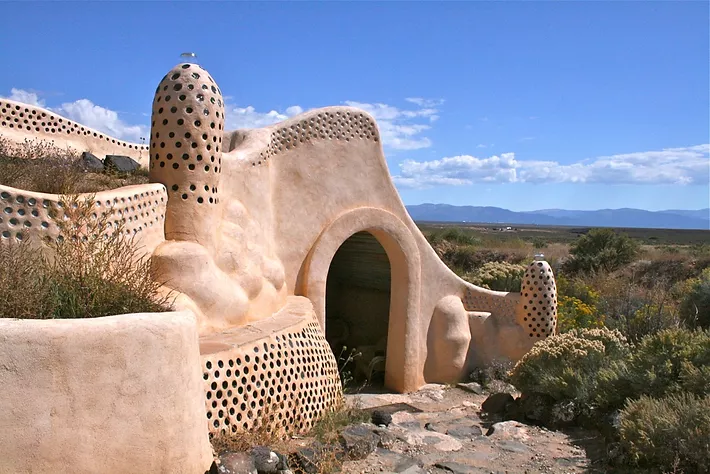

Choosing a Location
Earthships are not suitable for all climates, since wet conditions may create internal mold issues. If you live someplace with everchanging weather, a backup power sources for fall and winter may be needed when there is not enough sun for your solar energy panels.
Straw Bale Homes
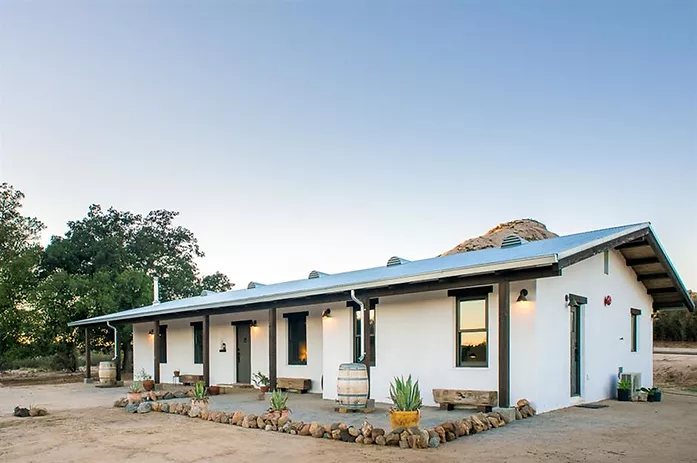

Image via SimpleConstruct
Straw Bale homes use straw waste as insultation material. This home type reduces home building costs and provides excellent insulation and through eco-friendly, biodegradable straw material.
These houses were a temporary invention among the 19th-century farmers who relied on wheat crop waste as the only construction material. However, straw bale houses have been tested and confirmed to be comfortable, warm, and durable giving them recent popularity.
Click here to access a comprehensive Guide by on building a straw bale home.
Benefits of Straw Bale Homes

Image via Julia Furlong
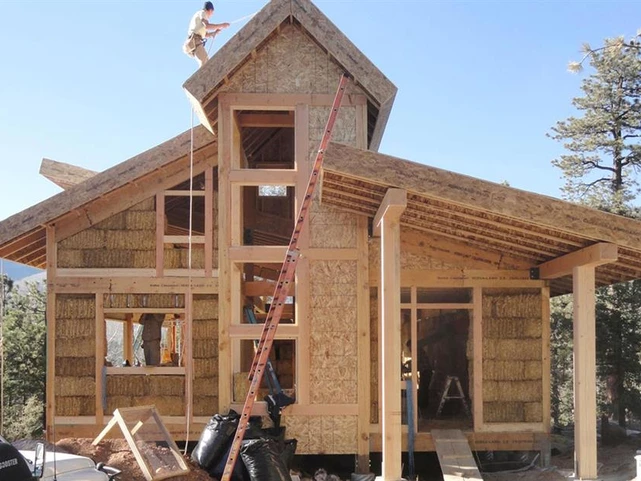

Image via DeepGreenArchitecture
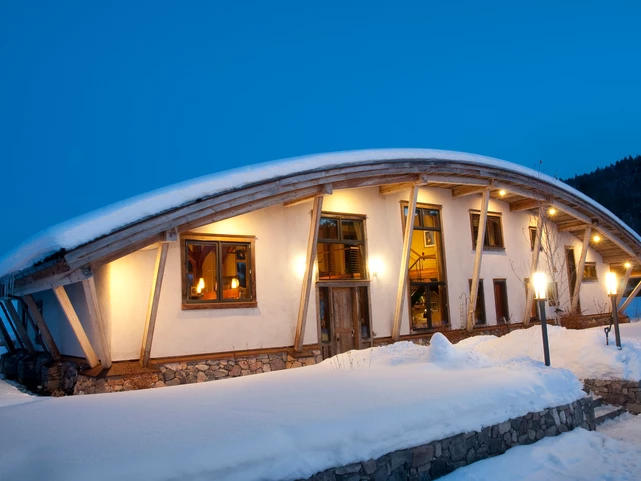

Image via Teton Timberframe
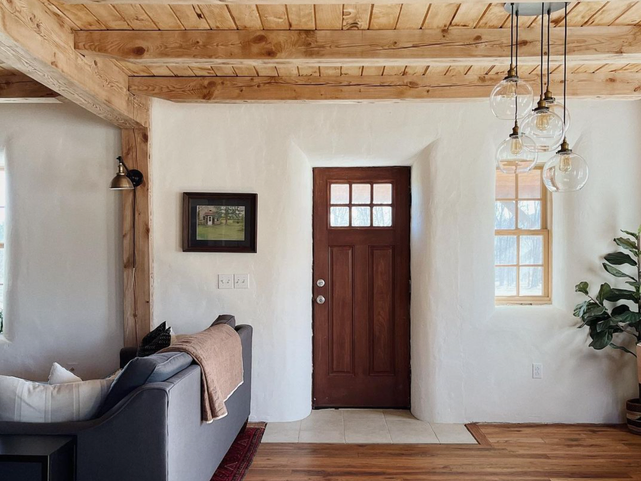

Image via Julia Furlong
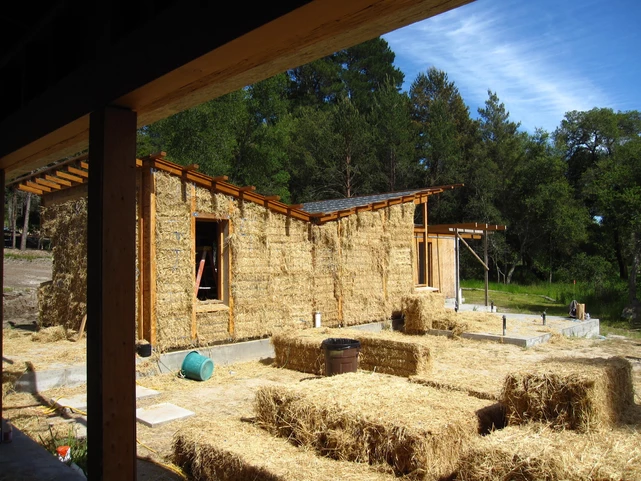

Image via Medium
How it Works
Straw Bale homes can last over 100 years if properly built and maintained. With insulation values of R-30 to R-35 or more, straw bale offers great insulation and comfort for your home.
Straw bale walls are at least eighteen inches thick, giving your home extra aesthetic value to the home since thick walls are expensive to achieve with traditional construction. The thicker the bale, the better the R-value.
What weather is best for straw bale homes?
If your straw bale home is constructed properly, it won’t rot since the porous texture allows air circulation. If you live in an especially humid area, lime-based plasters work best to keep moisture at bay. However, these homes are not recommended for areas with extreme rain and moisture.
Click here to access a comprehensive Guide by on building a straw bale home.
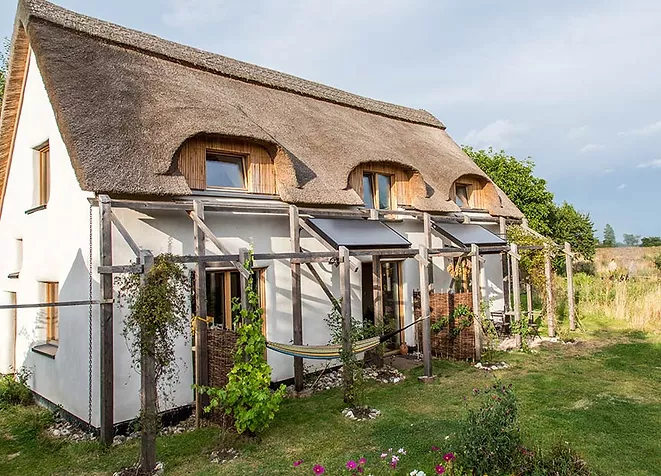


Image via Passive House Plus
What Else Should I Consider?
Click here to learn more about design criteria and considerations. Here are some tips to keep in mind:
-
If your local building codes do not have regulations for building with straw bale, you may face planning challenges. This might require working with local engineers and architects who are familiar with natural materials to help in gaining this approval.
-
Due to the thickness of straw bale, most of your square footage will be taken up by the wall thickness.
-
If straw bale material is not locally available, you may have additional shipping costs and the additional challenge of ensuring they arrive intact
Straw bales are a natural and renewable material with a significantly lower environmental footprint than most other types of insulation materials
Adobe Homes
Adobe homes can be traced back to 8300 B.C. , making them the oldest continually inhabited structures in the world.
Earth-based and local materials, such as mud, clay, and straw, make the bricks used to construct the walls of traditional Adobe homes. These homes can offer fireproof, biodegradable structures that are long lasting and built with low-energy. They have thick, round-edged walls with small, square windows that reflect the look of traditional Indian Pueblos.
What Benefits do Adobe Homes Offer?
Costs and Other Considerations

Costs can range from $55-85 per square foot, using salvaged and saved materials, a simple design and a few custom touches.
Adobe homes are some of the cheapest and most eco-friendly earth homes to build due to reduced costs of locally sourced materials. The amount of energy required to make one adobe brick is 30 times less than the energy required to produce one kiln-baked conventional brick since they are solidified with outdoor heat.
Weather and Climate
Given the environment factors needed to efficiently produce adobe bricks, adobe buildings are primarily confined to warm and dry places.
Limited regions in the world offer the conditions needed for adobe homes: prolonged periods of fairly hot and dry weather. Trying to rush the process to dry adobe bricks by setting them close to a fire will result in uneven heating and cracking, while a slow drying time creates other structural issues.
Adobe buildings are not very common in places with cold winters since adobe walls lack the insulation needed when temperatures dip.

Image via Christies Real Estate
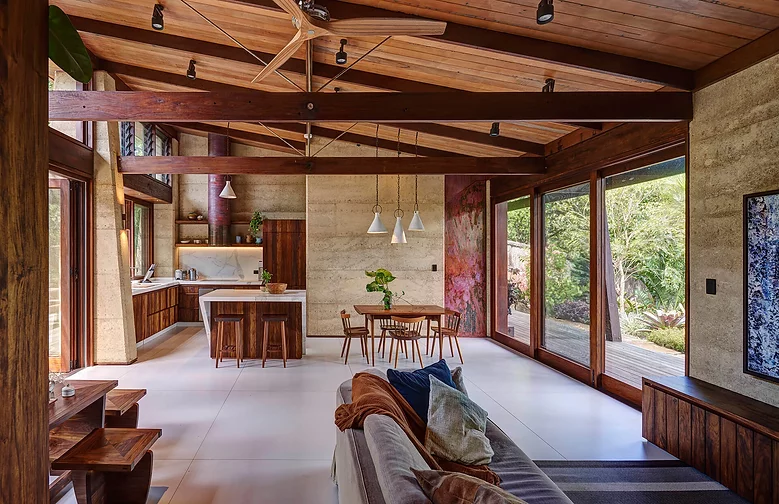
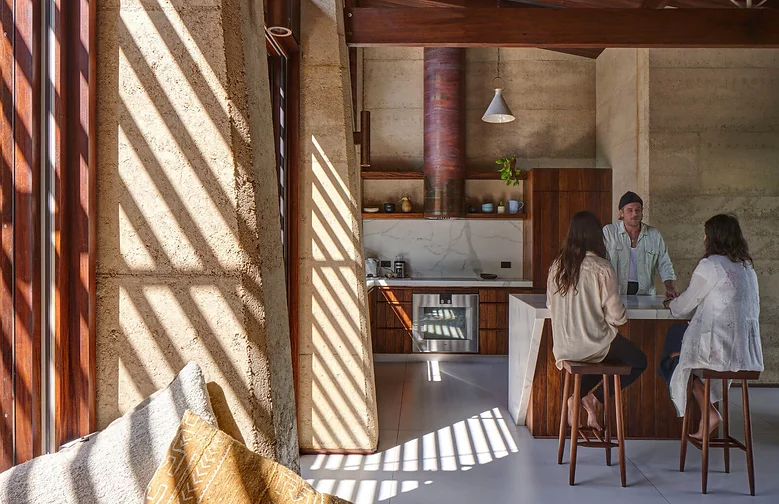
Rammed Earth Homes

Image via Dwell
Rammed homes are made of damp soil or earth that is placed in formwork, and then compressed or rammed into a solid, dense wall.
Rammed earth construction almost disappeared with the development of reinforced concrete, but there has been a revival in interest because of its aesthetics and the environmental benefits they offer.

Image via Dwell
How Does it Work?
Rammed earth homes are like building sand a castles without that having to flip the bucket. Instead, the form of the home is already in place with a plywood structure and if filled with earth materials to create the walls.
A mix of soils is rammed into the structure, which is reinforced through structural engineering. When everything is packed tightly, the plywood structure is removed and leaves a solid, stable wall. Builders ram and repeat until the entire house is built.
Benefits and Challenges of Rammed Earth Homes
Comfort
and
Eco-Friendliness
Rammed earth is non-toxic, non-polluting and ‘breathes’. This creates safer, more people-friendly buildings. It is very low in embodied energy, and extremely comfortable to live in.
Low Maintenance
Once they are built and sealed, they shouldn’t need any further attention for at least 10-20 years. Rammed earth walls are features that stand alone and don’t need finishing with plasterboard or render, inside or outside.
Manual Labor Costs
A wall system in a rammed earth home can cost about 30 percent to 50 percent more than a conventional wood-frame house due to manual labor, which means the entire home might cost about 5 percent to 15 percent more
Thermal Mass and
Climate Challenges
Rammed earth has high thermal mass but low insulation. This makes rammed homes good for desert like environments but challenging in places with prolonged cold weather and rain. This factors might require additional insulation, as well as a larger roof, so that the overhangs protect the earthen walls.
Costs of Rammed Earth Homes
The initial cost of rammed earth construction is comparable to conventional masonry construction, however the longevity of rammed earth homes far passes that of traditional homes.
The average stick-frame home has a life span of 49 years, while a properly built rammed earth house can last 1000+ years. The primary factors affecting the cost are design and site characteristics.

Did You Know?
In modern rammed earth 5-10 % cement is added as specified by an engineer. Rigid insulation is oftentimes inside the rammed earth wall for thermal resistance as well as steel for seismic reinforcement.
image via Dwell
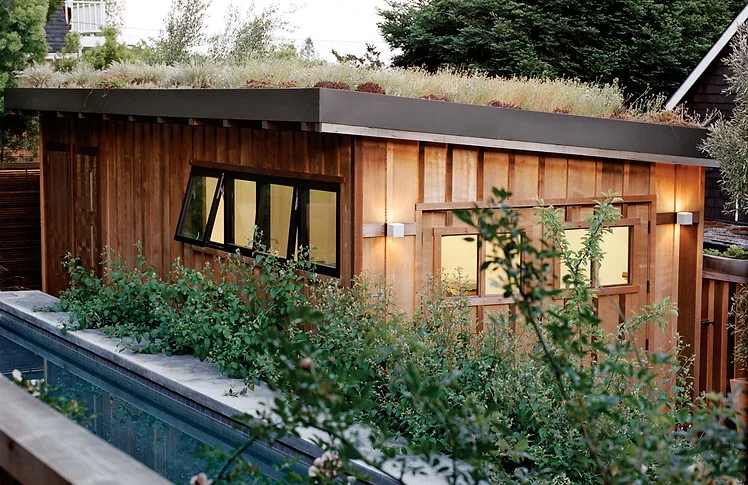
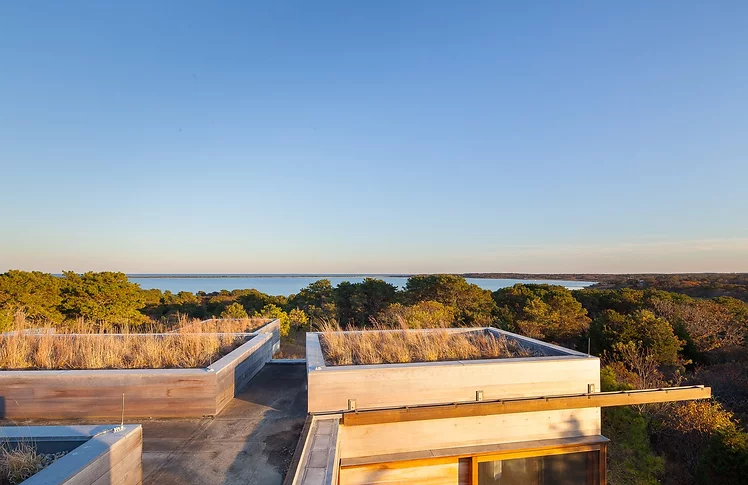
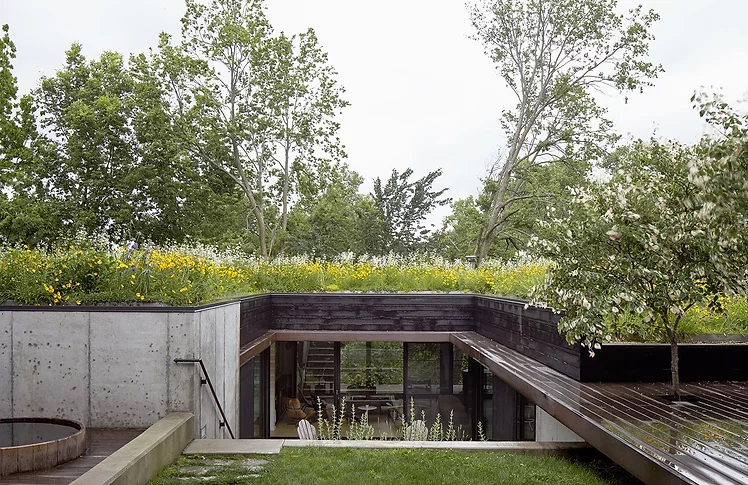
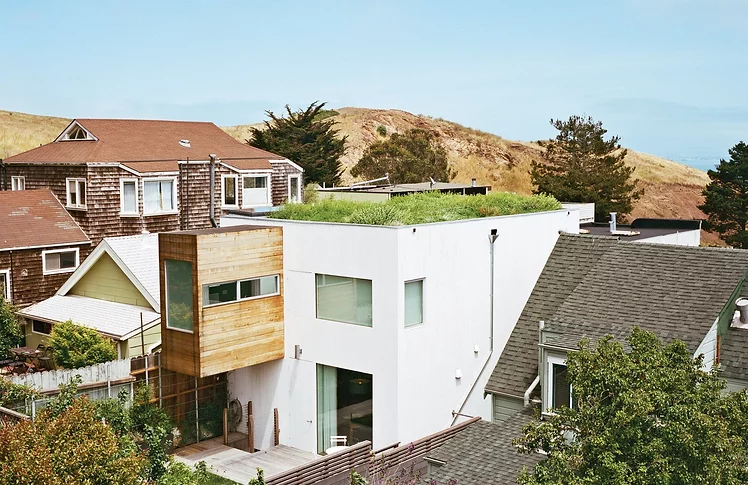
Green Roof Homes
Green roofs, or 'living roofs', are rooftops covered with living vegetation planted in lightweight engineered soil.
Green roofs involve more than tossing plants on the roof and letting them grow. These roofs require drainage material and a waterproof membrane along with careful plant selection. Scroll to read about benefits and challenges of green roofs
Why Green Roofs?
Green roofs serve several purposes:
-
reducing storm water runoff
-
creating a habitat for wildlife
-
reducing the need for heating and cooling
-
decreasing stress of the people who visit the roof by providing an relaxing and natural landscape
-
providing acoustic insulation
-
lowering urban air temperatures and GHG.
Did You Know?
Newark, NJ was the next closest city with nearly 600,000 square feet of green roofs. The cities rounding out the top 10 are New York City; Seattle; Portland, OR; Toronto; Philadelphia; Chicago; Culpeper, VA; and Gaithersburg, MD.
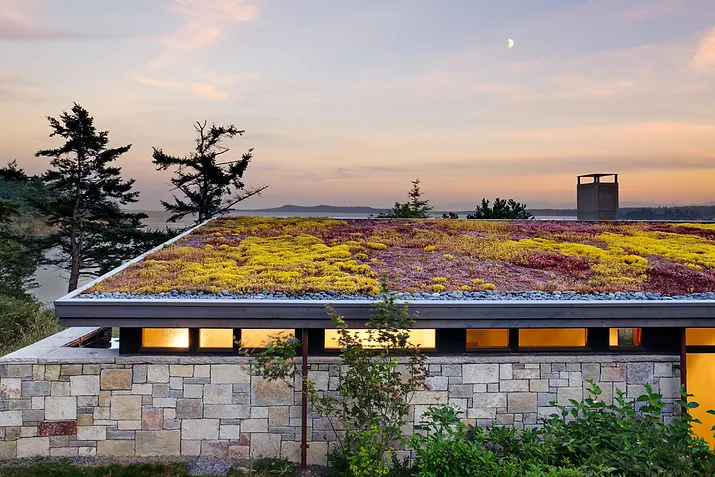

Photo via Houzz
Challenges of Green Roofs
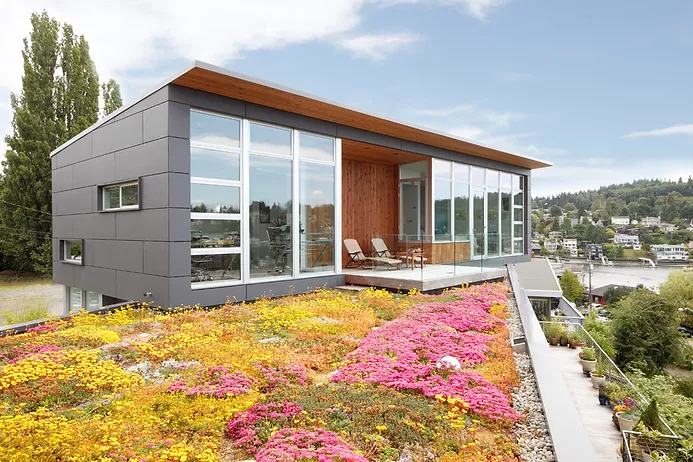

Photo via Houzz
Green roofs offer many benefits, but there are some added structural challenges that are important to consider:
-
A greater expense than traditional roofs. They tend to be slightly more expensive than the traditional option, but can also help you save money on energy
-
An increase in weight load. Green roofs are heavier and as such, require more structural support to be implemented
-
A yearly inspection to remove problematic shrubs helps reduce the potential for developing leaks
-
limited plant choices for extensive green roofs
Types of Green Roofs + Costs
The longevity of green roofs has the greatest effect on savings, whereas installation and maintenance have the greatest effect on cost (maintenance costs are even greater than the installation premium).
Recover Green Roofs has found that extensive roofs can cost about $10 to $50 per square foot, while intensive roofs can cost from $20 to $200+ per square foot.
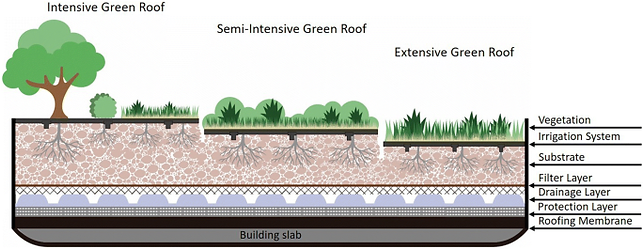
Image via Circular Economy and Resilience
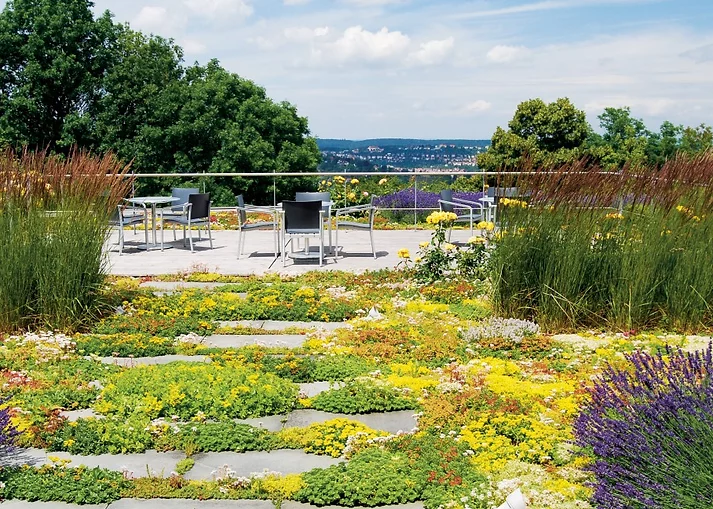

Image via Urban Green Blue Grids
-
3- 6″ of light weight growing medium.
-
low-maintenance ground-cover plants.
-
ideal for large flat-roof buildings and apartments.
-
suitable for low-sloped residential roofs and retrofits.
-
desert grasses and succulent plants.
-
after one year, they do not require watering.
-
annual spring weeding of tree seedlings & weeds – brought in by birds and wind.
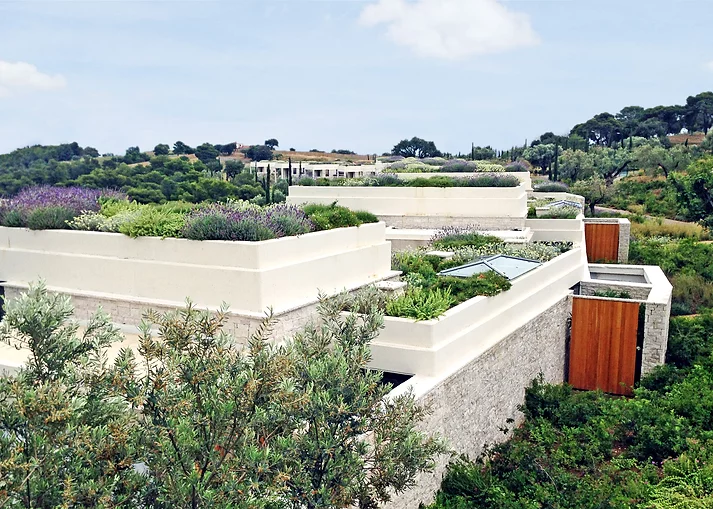

Image via Zinco Green Roof
-
also known as rooftop gardens
-
8-12 inches, or more, of growing medium.
-
fully landscaped roof top garden.
-
diverse plants and trees can be planted (avoids plants with invasive root systems).
-
walkways, railings and lighting can be incorporated
-
parks, playgrounds or vegetable gardens can be built
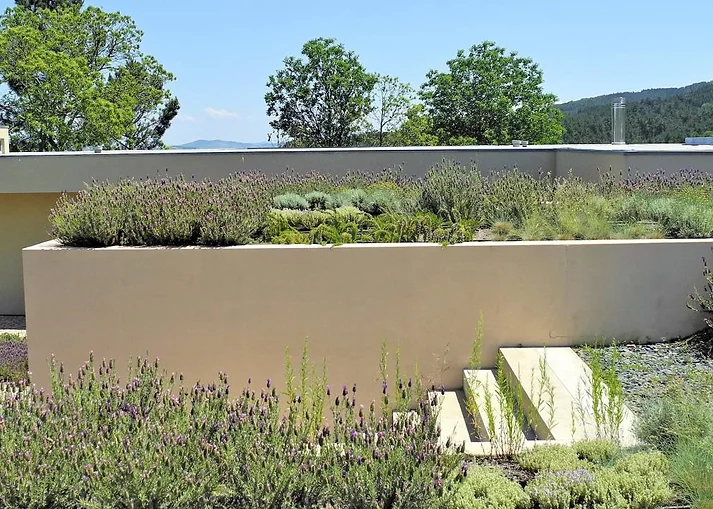

Image via Zinco-Green Roof
-
Semi-intensive roofs, combinations of both extensive and intensive green roofs, are typically adopted to harness both the environmental benefits of a green roof, as well as a diverse garden within a manageable maintenance budget.
-
ideal for long-term care facilities, daycare play spaces, employee picnic areas, and urban agriculture



















